Receiving via SRT
The Secure Reliable Transport (SRT) protocol is an open-source video streaming protocol designed to provide low-latency, high-quality video streaming over unreliable networks. SRT uses end-to-end encryption and provides a range of features designed to enhance reliability and security, including error correction, congestion control, and retransmission of lost packets. SRT is often used for live video streaming applications, such as sports and news broadcasts, where maintaining a reliable, high-quality connection is critical.
Address format
Section titled “Address format”SRT can be received in two modes:
Caller mode- Astra sends a request to the SRT server and receives content in response. This is the most popular variantListener mode- Astra waits for the SRT server to establish a connection and receives content in the request. This is a point-to-point mode
The address format depends on the selected mode.
Caller mode
Section titled “Caller mode”srt://address:port[#options]address- remote server IPv4 address or hostnameport- remote port
Example:
srt://example.com:3001- send request to example.com
Listener mode
Section titled “Listener mode”In listener mode, the address format is similar to the UDP address, with the addition of the @ symbol to indicate the local interface name.
srt://[interface]@:port[#options]interface- local interface name where to listen for connection. By default, Astra waits for a connection on all interfacesport- local port to accept incoming connectionsoptions- additional options for SRT protocol
Examples:
srt://@:3001- wait for connection on any interfacesrt://eth0@:3001- wait for connection on interfaceeth0
Options
Section titled “Options”timeout=N- restarts the receiver if no data is received within a defined interval, in seconds. Default:5secondslatency=N- maximum accepted transmission latency, in milliseconds. Default:120millisecondspacketfilter=S- injects extra processing instructions at the beginning and/or end of a transmission to implement Forward Error Correction (FEC). Read more{target=“_blank”} in the official documentationpassphrase=S– password for encrypted transmission. Length: 10-79 characterspbkeylen=N– crypto key length in bytes. Values: 16, 24, 32. Default:0streamid=ID– stream identifier provided to the SRT server in caller modeno_tsbpdmode– turns off timestamp-based packet delivery modeoheadbw- limits bandwidth overhead, in percent. Range: 5-100. Default:25
Web Interface
Section titled “Web Interface”To configure SRT reception, go to New Stream or the settings of an existing stream and set Input Type to SRT.
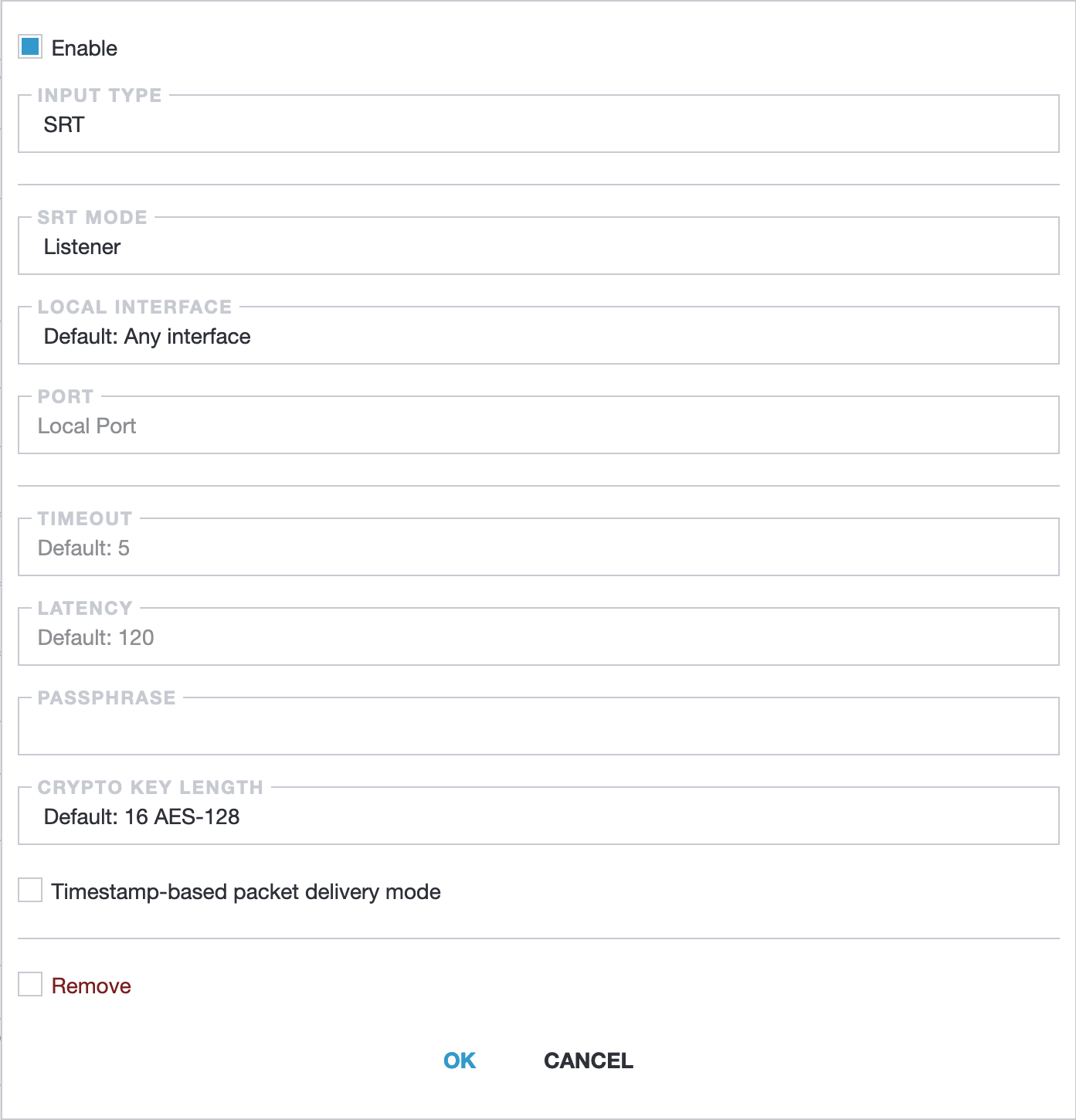
- Input type: Select SRT to enable SRT-specific configuration options.
- SRT mode: Determines whether Astra acts as a Caller or Listener. Select Listener to wait for incoming connections.
- Local interface: The network interface for receiving the stream. Default is Any interface.
- Port: The network port for receiving the stream.
- Timeout: Time in milliseconds to wait for incoming data before timing out. Default: 5000 ms (5 seconds).
- Latency: Delay in milliseconds to improve stability. Default: 120ms. Higher latency increases stability but adds delay. See Latency for SRT Receiving for more details.
- Passphrase: Password for secure communication. Must match the sender’s passphrase.
- Crypto key length: Length of the cryptographic key (16, 24, or 32 bytes). Default: 16 bytes (128 bits).
- Timestamp-based packet delivery mode: When enabled, uses timestamps to ensure correct packet order. Default: Disabled.